Figure 4
Download original image
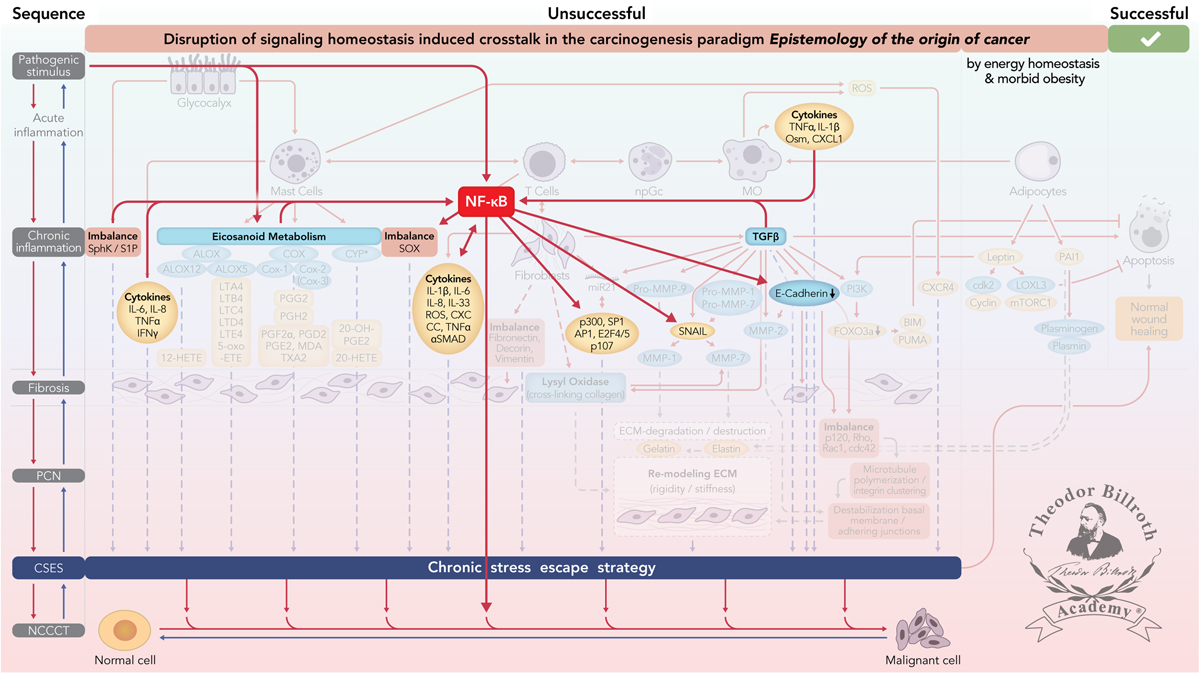
NF-κB signaling and crosstalk during carcinogenesis – Special Issue: Disruption of homeostasis-induced signaling and crosstalk in the carcinogenesis paradigm “Epistemology of the origin of cancer”. Simplified scheme of NF-κB signaling and crosstalk during carcinogenesis in the Disruption of signaling homeostasis induced crosstalk in the carcinogenesis paradigm “Epistemology of the origin of cancer” consisting of a six-step sequence: (1) a pathogenic stimulus followed by (2) chronic inflammation from which develops (3) fibrosis with associated remodeling of the cellular microenvironment; and from these changes a (4) precancerous niche (PCN), a product of fibrosis, with remodeling by persistent inflammation, develops which triggers the deployment of (5) a chronic stress escape strategy and when this fails resolve it by (6) normal cell to cancerous cell transition (NCCCT) by PCN-induced cell matrix stress occurs. This figure was published in paper 2 of this Special Issue [189] and modified in accordance to NF-κB signaling and crosstalk. Nomenclature: Common abbreviations are bold, followed by the common trivial names (if available) and (if available) by the name in accordance to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC): PCN: precancerous niche; CSES: chronic stress escape strategy; NCCCT: normal cell to cancerous cell transition; SphK: sphingosine kinase isoform; S1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate; IL-6: interleukin 6; IL-8: interleukin 8; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor alpha; IFNγ: interferon gamma; ALOX: lipoxygenase, arachidonate lipoxygenase; ALOX12: 12-lipoxygenase, 12-LOX, 12S-LOX, arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase 12S type; ALOX5: 5- lipoxygenase, 5-LOX, arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase; 12-HETE: 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; LTA4: leukotriene A4, 4-[(2S,3S)-3-[(1E,3E,5Z,8Z)-tetradeca-1,3,5,8-tetraenyl]oxiran-2-yl]butanoic acid; LTB4: leukotriene B4, (5S,6Z,8E,10E,12R,14Z)-5,12-dihydroxyicosa-6,8,10,14-tetraenoic acid; LTC4: leukotriene C4, (5S,6R,7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-6-[(2R)-2-[[(4S)-4-amino-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]-3-(carboxymethylamino)-3-oxopropyl]sulfanyl-5-hydroxyicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid; LTD4: leukotriene D4, (5S,6R,7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-6-[(2R)-2-amino-3-(carboxymethylamino)-3-oxopropyl]sulfanyl-5-hydroxyicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid; LTE4: leukotriene E4, (5S,6R,7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-6-[(2R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulfanyl-5-hydroxyicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid; 5-oxo-ETE: (6E,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5-oxoicosa-6,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid; Cox: cyclooxygenase; Cox-1: cyclooxygenase 1; Cox-2: cyclooxygenase 2; Cox-3: isoform of Cox-2 (therefore in brakes); PGG2: prostaglandin G2, (Z)-7-[(1S,4R,5R,6R)-5-[(E,3S)-3-hydroperoxyoct-1-enyl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-6-yl]hept-5-enoic acid; PGH2: prostaglandin H2, (Z)-7-[(1S,4R,5R,6R)-5-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-6-yl]hept-5-enoic acid; PGFF2α: prostaglandine F2 alpha, (Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxy-2-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]cyclopentyl]hept-5-enoic acid; PGD2: prostaglandin D2, (Z)-7-[(1R,2R,5S)-5-hydroxy-2-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]-3-oxocyclopentyl]hept-5-enoic acid; PGE2: prostaglandin E2, (Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]-5-oxocyclopentyl]hept-5-enoic acid; MDA: malondialdehyde, propanedial; TXA2: thromboxane A2, (Z)-7-[(1S,2S,3R,5S)-3-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]-4,6-dioxabicyclo[3.1.1]heptan-2-yl]hept-5-enoic acid; CYP*: cytochrome P450 isoforms; 20-OH-PGE2: 20-hydroxy prostaglandin E2; 20-HETE: 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-20-hydroxyicosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid; SOX: [sex-determining region Y (Sry) box-containing] transcription factor family; IL-β1: interleukin beta 1; IL-33: interleukin 33; ROS: reactive oxygen species; CXC CC: chemokine receptors; αSMAD: alpha-smooth muscle actin; miR21: micro RNA-21; p300: protein 300 (p300-CBP coactivator family); SP1: specificity protein 1; AP1: activator protein 1; E2F4/5: cytoplasmic complex of Smad3, retinoblastoma-like protein 1 (P107, RBL1), E2F4/5 and D-prostanoid (DP1); p107: retinoblastoma-like protein 1, RBL1; TGFβ: transforming growth factor beta; Pro-MMP-9: pro-matrix metalloproteinase 9; Pro-MMP-1: pro-matrix metalloproteinase 1; Pro-MMP-7: pro matrix metalloproteinase 7; SNAIL: zinc finger protein SNAI1; MMP-1: matrix metalloproteinase 1; MMP-7: matrix metalloproteinase 7; MMP-2: matrix metalloproteinase 2; E-Cadherin: CAM 120/80 or epithelial cadherin, cadherin-1, epithelial cadherin; CXCL1: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1; Osm: oncostatin-M; PI3K: phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; FOXO3a: forkhead box protein O3a; p120: catenin delta-1, protein 120; Rho: Ras homolog gene family, member A; Rac1: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; cdc42: cell division control protein 42 homolog; BIM: Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death; PUMA: BH3-only protein; CXCR4: C-X-C motif of chemokine receptor 4; cdk2: cyclin-dependent kinase 2; LOXL3: lysyl oxidase homolog 3; mTORc1: rapamycin complex 1; PAI1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.

