| Issue |
4open
Volume 1, 2018
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 5 | |
| Number of page(s) | 11 | |
| Section | Chemistry - Applied Chemistry | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/fopen/2018005 | |
| Published online | 12 November 2018 | |
Research Article
Characterization and modeling of the polarization phenomenon to describe salt rejection by nanofiltration
1
Membrane Technology Laboratory, Water Researches and Technologies Centre of Borj-Cedria (CERTE),
Technopark of Borj-Cedria,
8020
Soliman, Tunisia
2
Higher Institute of Sciences and Technologies of Environment of Borj Cedria, University of Carthage, Carthage, Tunisia
3
Tunisia Faculty Science, Tunis, Tunisia
* Corresponding author: yassinemdemagh@yahoo.fr
Received:
9
February
2018
Accepted:
3
October
2018
In this work, dead-end filtration was applied to the nanofiltration of synthetic ionic solutions. In order to study the phenomenon of polarization in the boundary layer, we chose NaCl, CaCl2 and Na2(SO4) solutions to pH = 6.8 which concentrations varies from 0.3 to 1.5 g L−1 and the filtration pressure varied from 6 to 16 bar. In this study, the results of these experiments show a correlation between the initial concentration of the solution and the pressure applied with the polarization. The polarization intensifies for the high concentrations and pressures. The ionic balance between the microscopic zone of polarization and the macroscopic state of the solution is described by the following key equation of the model:
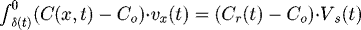
The novelty of this model that it is sufficient to know the conductivity and volume flow of permeate solution to calculate precisely the polarization concentration at the membrane surface, the thickness of the polarization layer and the concentration profile inside the boundary layer polarization. It is important to note that the model developed does not take into account the clogging phenomenon because the experiments were done on low concentration synthetic ionic solutions.
Key words: Nanofiltration / Polarization / New model
© Y. Mdemagh et al., Published by EDP Sciences 2018
 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

